Developer Guide
Libmgr is a desktop app for managing the inventory of libraries, optimised for use via a Command Line Interface (CLI). Designed for fast typists, it can help to augment the day-to-day tasks of a librarian and can help them to get tasks done in an efficient manner.
This document is meant to assist developers in better understanding the inner workings of the program.
- Acknowledgements
- Setting up the project
- Design
- Implementation
- Appendix A: Product Scope
- Appendix B: User Stories
- Appendix C: Non-Functional Requirements
- Appendix D: Instructions For Manual Testing
Acknowledgements
The format of this developer guide was adapted from SE-EDU AddressBook Level 3 Developer Guide
Libmgr also makes use of the following third-party libraries:
- Jackson Databind Provides serialization and deserialization to and from JSON (Apache 2 License)
- Jackson Annotations Provides serialization and deserialization to and from JSON (Apache 2 License)
- Jackson Datatype JSR310 Adds support to Jackson Databind for Java 8 Date/Time API (Apache 2 License)
Setting up the project
Prerequisites
Before setting up the project locally, ensure you have installed the following:
- Java JDK 11
- IntelliJ IDEA
⚠ Caution: Follow the steps in the following guide precisely. Things will not work out if you deviate in some steps.
First, fork this repo, and clone the fork into your computer.
If you plan to use Intellij IDEA (highly recommended):
- Configure the JDK: Follow the guide [se-edu/guides] IDEA: Configuring the JDK to ensure Intellij is configured to use JDK 11.
- Import the project as a Gradle project: Follow the guide [se-edu/guides] IDEA: Importing a Gradle project to import the project into IDEA. ⚠ Note: Importing a Gradle project is slightly different from importing a normal Java project.
- Verify the setup:
- Run the
seedu.duke.Libmgrand try a few commands. - Run the tests to ensure they all pass.
- Run the
Design
This section provides an overview of the design architecture and design of the various components of Libmgr.
Architecture
The following Architecture Diagram provides a high level visualization of the interaction between the various components of the app. Further elaboration is given below.
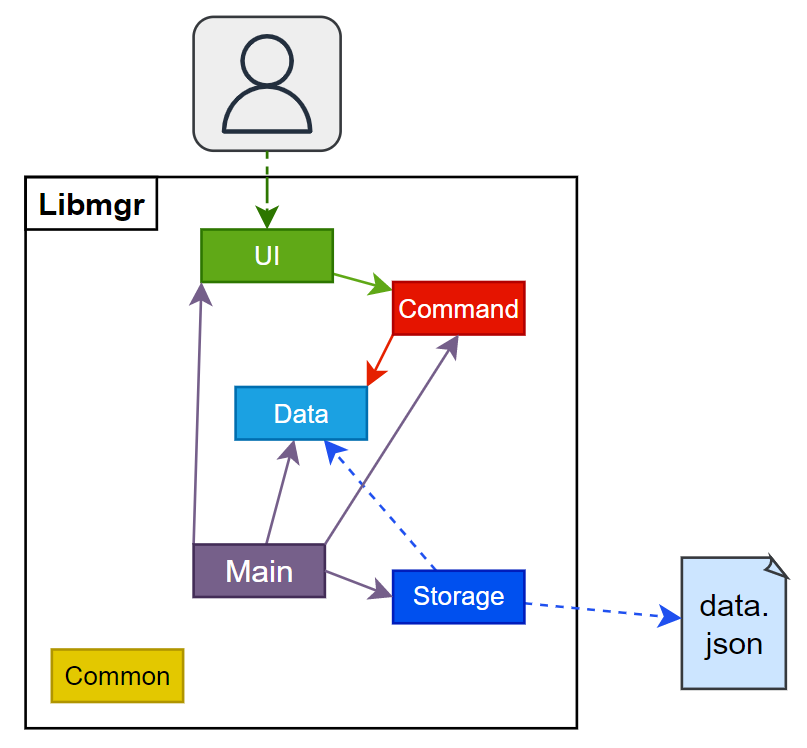
The base Libmgr class consists of the main method which is responsible for:
- Application launch: initializing the components in the correct order and setting up the data containers effectively.
- Application teardown: shutting down the components, perform cleaning up and closing of processes where necessary.
Beyond that, the libmgr application contains a number of other components:
ui: Contains TextUI, the class which handles user interaction through the command line UI .data: Contains the library catalogue and various item classes that form the data of the app along with all relevant operations.commands: Contains various command classes that facilitate the execution of commands and a parser class that parses user inputs.storage: Reads data from, and writes data to the hard disk.common: Contains a collection of classes used by multiple other components, such as exceptions and messages.
Application Launch
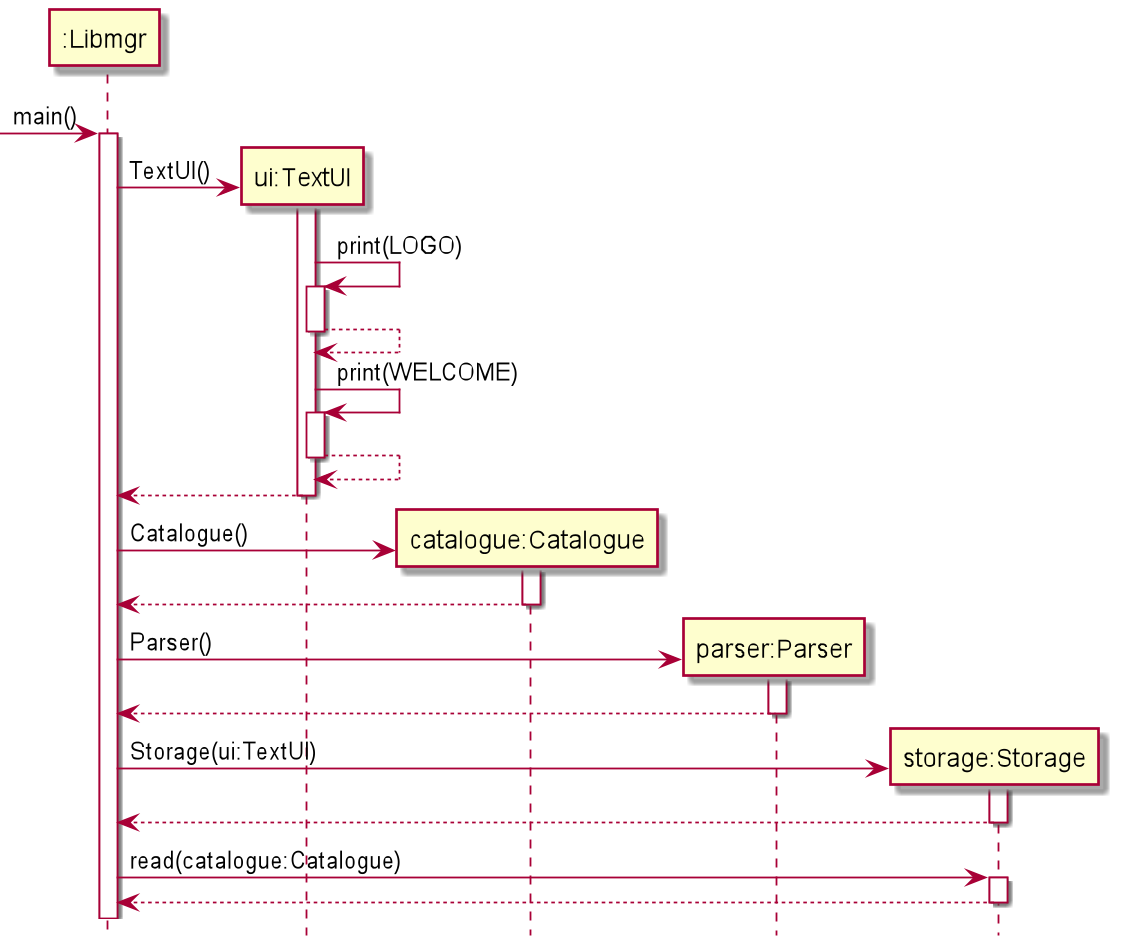
The above sequence diagram depicts how the components interact with each other when the program is first started.
- A
TextUIobject is created which then prints the logo and a welcome message. - The
Cataloguecontainer is created in order to store all items. - A
Parserobject is created. - A
Storagehandler is created, before havingread()called to load in existing data fromdata/data.json(if applicable).
Component Interaction
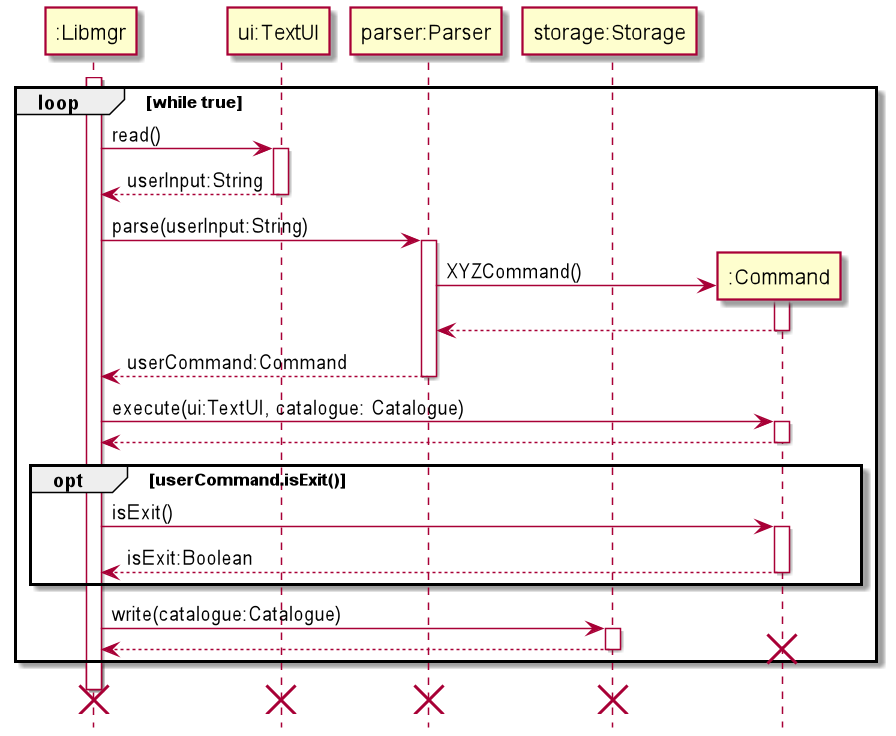
The above sequence diagram shows the interactions occurring each time a command is issued by the user.
Libmgruses theTextUIclass to obtain the user input.Libmgrthen usesParserto parse the user input.- A
Commandobject is returned based on the user input. Libmgrthen calls theexecute()method of theCommandobject which performs all the logic as defined by the command- The exit condition is checked by computing whether the
isExit()method of the currentCommandobject returns true. If it is computed as true, the loop is broken out of and the program quits. Libmgrlastly calls thewrite()method of theStorageobject which writes the current state of teh items in theCataloguecontainer todata/data.json
Commands component
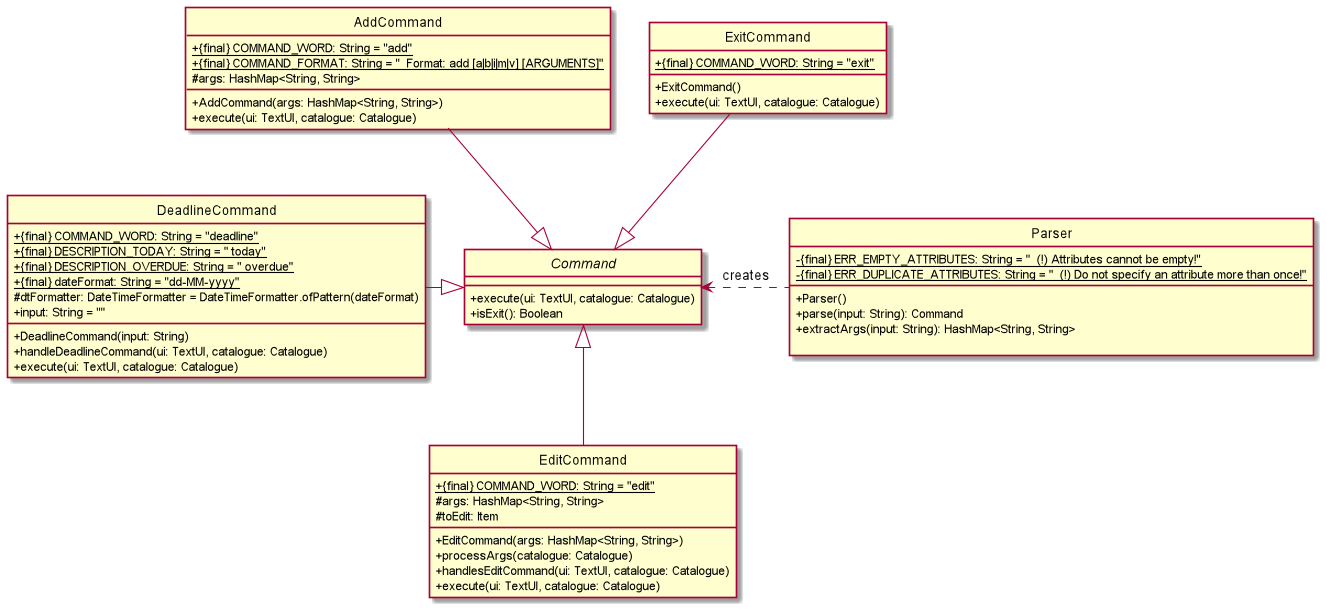
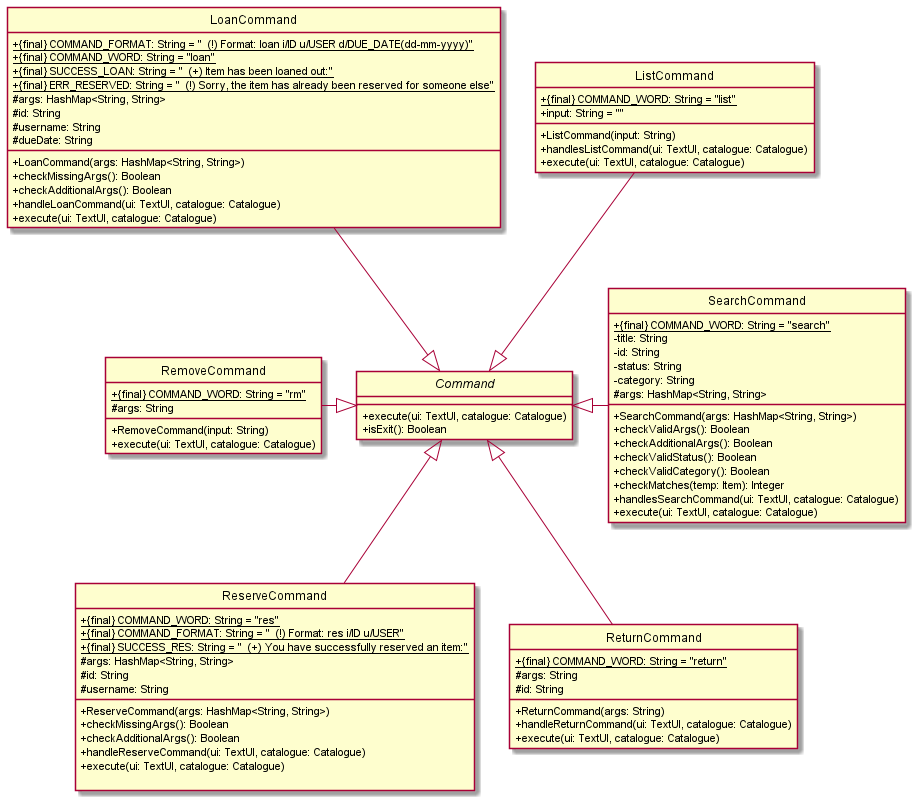
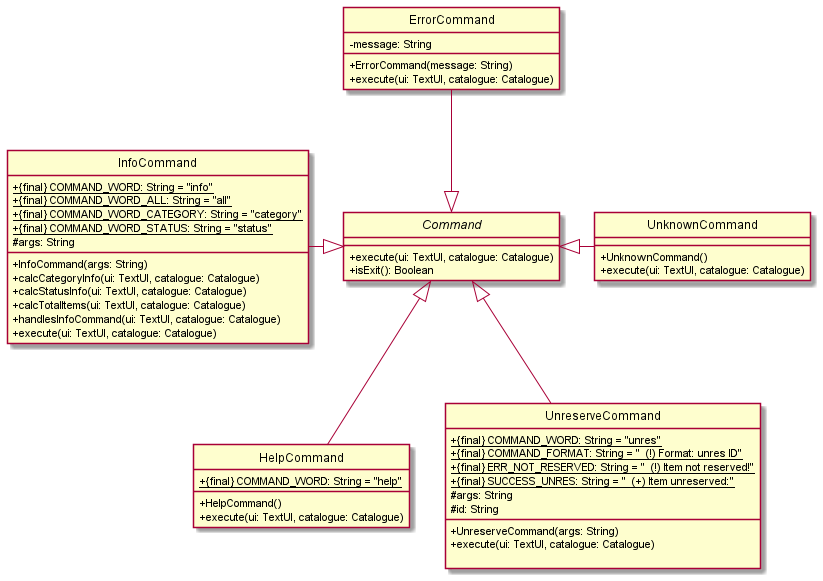
The above partial class diagrams illustrate the classes inside the commands component that correspond to specific functionalities.
The commands component consists of a commands package. Inside the package are the following classes:
- A main
Parserclass to process all the commands - An abstract
Commandclass, from which all other individual command classes inherit from - Individual Command classes, each corresponding to a specific command based on the user input
AddAudioCommandAddBookCommandAddCommandAddMagazineCommandAddMiscellaneousCommandAddVideoCommandDeadlineCommandEditAudioCommandEditBookCommandEditCommandEditMagazineCommandEditMiscellaneousCommandEditVideoCommandErrorCommandExitCommandHelpCommandInfoCommandListCommandLoanCommandRemoveCommandReserveCommandReturnCommandSearchCommandUnknownCommandUnreserveCommand
Each individual command class overwrites the execute(TextUI ui, Catalogue catalogue) method in the abstract Command class
to implement its own execution functionality.
Data Component
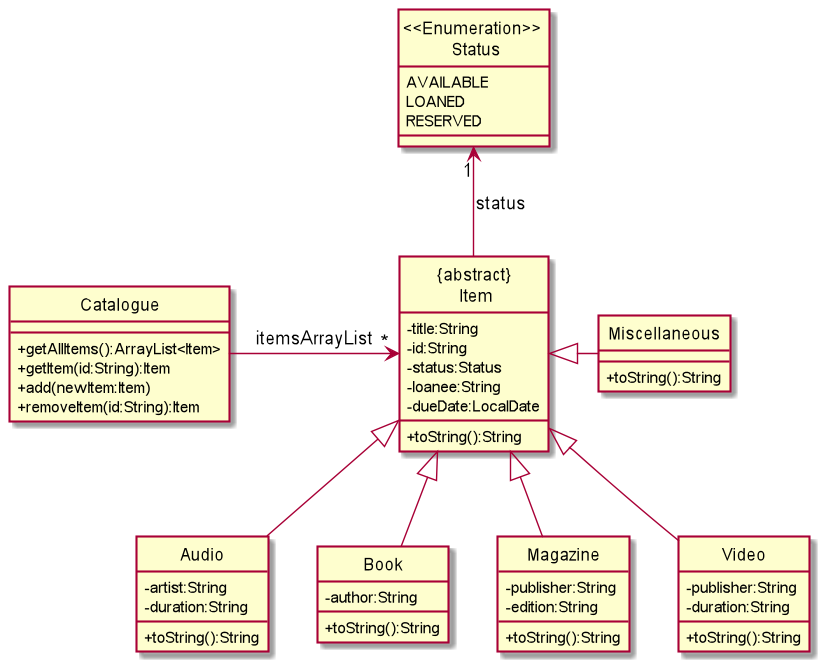
The data component consists of a data package which holds classes that allows the categorisation of items into different types.
- Audio
- Books
- Magazines
- Videos
- Miscellaneous
Additionally, this component also holds a Catalogue class, which acts as a container for all items and also provides functionality to perform operations on them.
Storage Component
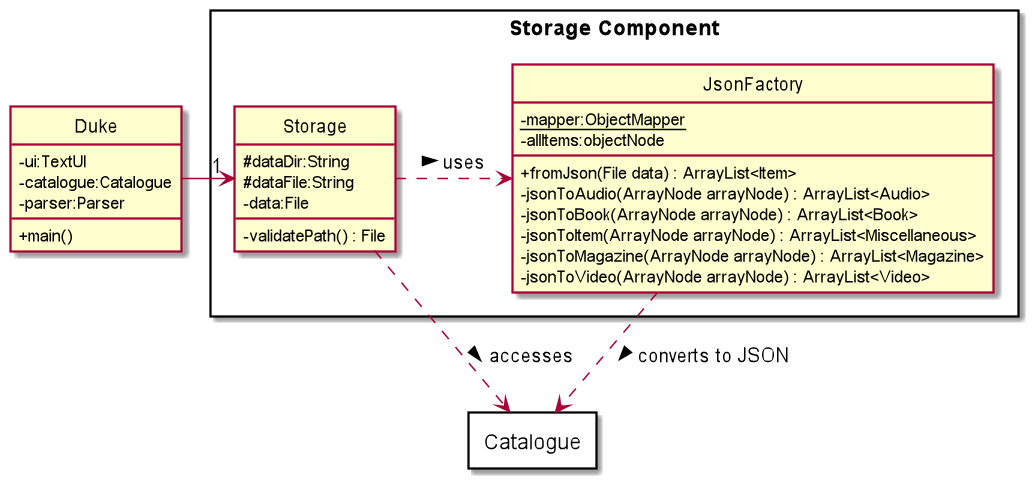
The storage component contains the Storage and JsonFactory classes.
Storageholds the functionality to write the current state of the catalogue to thedata.jsonfile. It also reads from thedata.jsonfile if one is found, if not a new empty file is createdJsonFactorycontains all the logic for deserializing theCatalogueobject into JSON so that it can be written into a file. Likewise, it also contains the logic for serializing theCatalogueobject when provided JSON. Furthermore, it also contains error checking to ensure that malformed or corrupted data is not processed.
ℹ️The directory and filename of the JSON file is defined within the
Storageclass
The default value is set to./data/data.json
UI Component
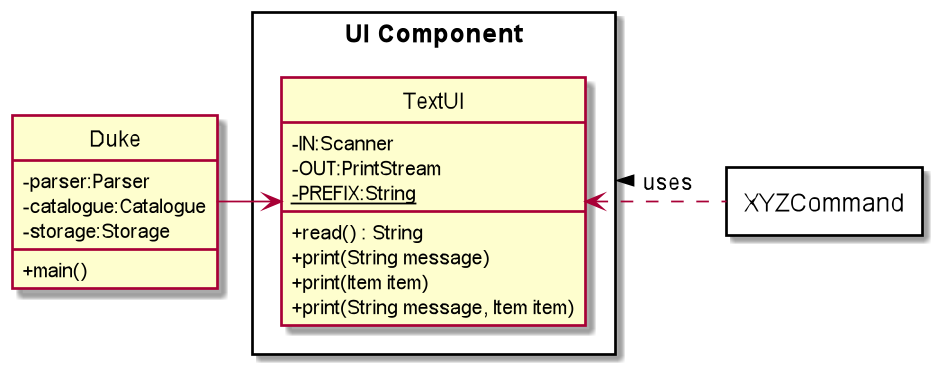
The UI component consists of a single TextUI class and is responsible for retrieving user inputs and displaying user feedback such as successful execution of commands, results of queries or details about exceptions.
Common component
Classes used by multiple components are located in the common package.
LibmgrExceptionis the main exception class for the app.Statusenumeration contains the possible values forStatusof items, which includeAVAILABLE,RESERVEDandLOANEDMessagescontains information, warning and error messages
Implementation
Add Command
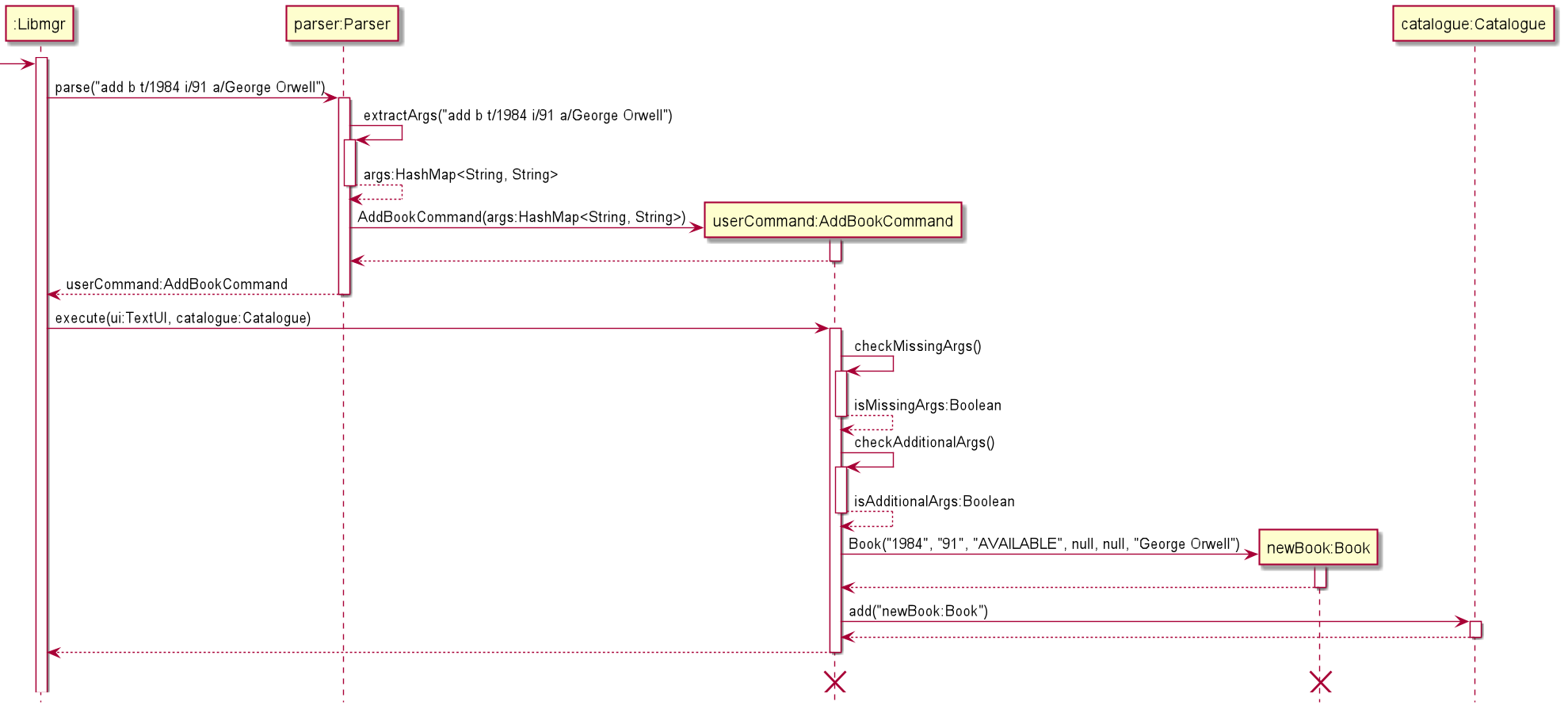
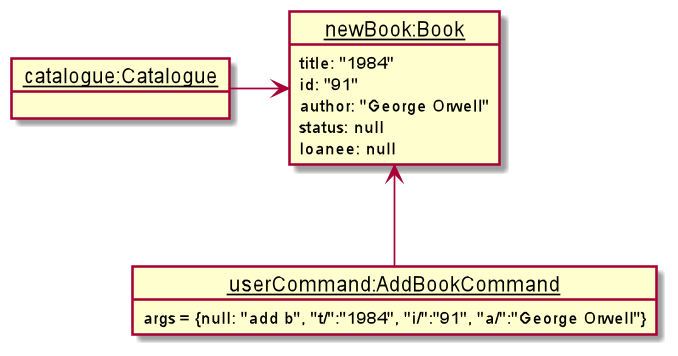
The following diagram shows the sequence diagram and the object diagram of the addition of a book. Firstly the user types in an add command.
The example which is shown in the above diagrams is the addition of a book with the title 1984, ID 91 and authored by George Orwell,
with the full command being add b t/1984 i/91 a/George Orwell
- The
main()method withinLibmgrcallsparser.parse(), supplying the full line of input entered by the user. - Within
parser.parse(),parser.extractArgs()is called on the line of user input, generating aHashMap<String, String>
In this instance, the hashmap will contain the following entries
| Key (String) | Value (String) |
|---|---|
| null | add b |
| t | 1984 |
| i | 91 |
| a | George Orwell |
- It then checks the value associated with the
nullkey in order to determine whichCommandto generate, in this case theAddBookCommandis generated - The newly created
AddBookCommandobject is returned by theparser AddBookCommand.execute()is executed byLibmgrwhich performs two checks, whether there are missing arguments and whether there are additional arguments supplied, outputting the relevant warning messages afterwards.- If both checks pass, a new
Bookobject is created with values stored in theHashMap<String, String>variable. - Lastly this new
Bookobject is passed to theCatalogueobject which along with theCatalogue.add()method.
Edit Command
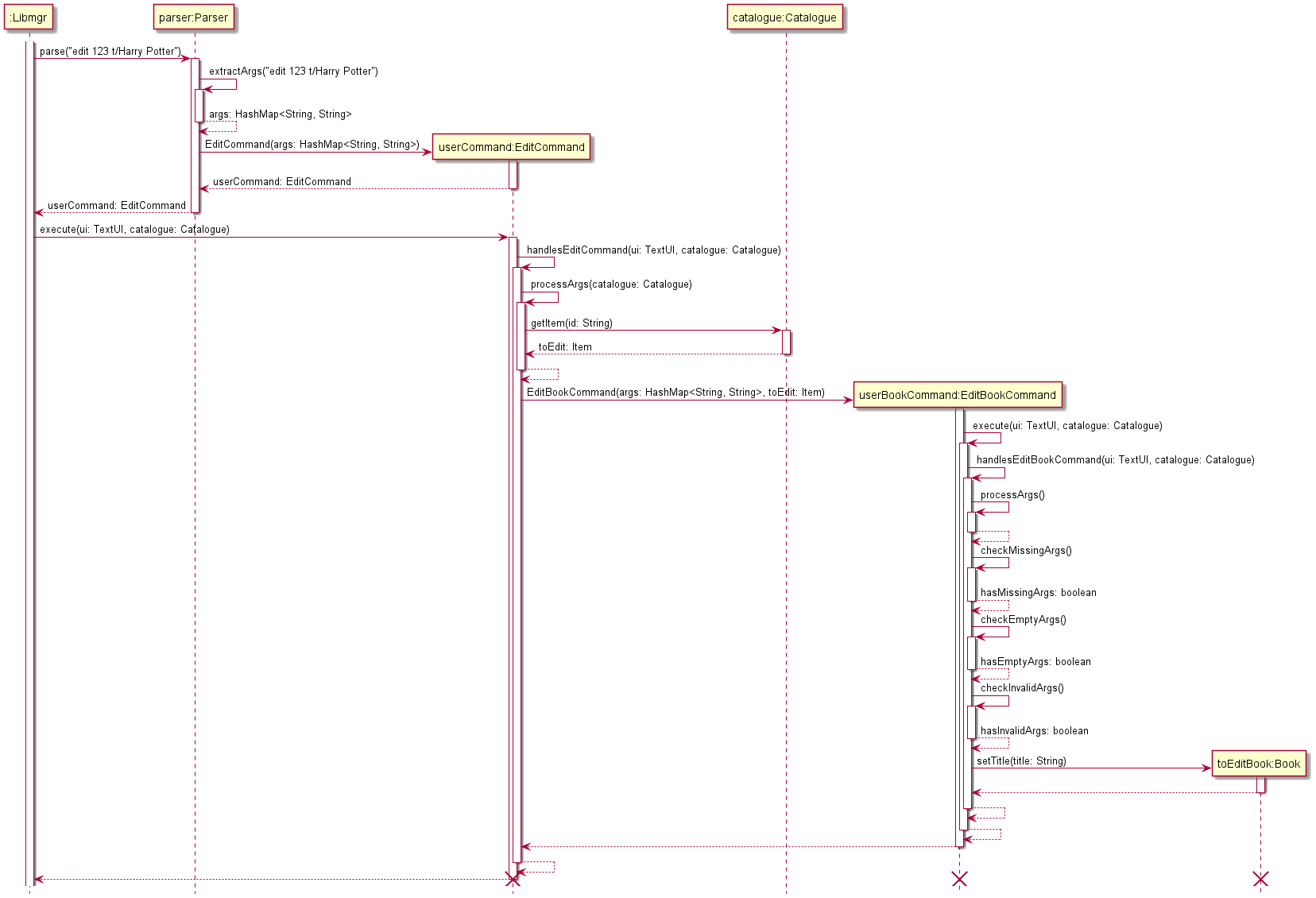
The Edit Command class handles the functionality to change a specific attribute of an item in the catalogue. The sequence diagram above shows the execution when the title attribute of a book with id 123 to “Harry Potter”.
Firstly, the user types in the edit command: edit 123 t/Harry Potter.
- The
main()method in Libmgr callsparser.parse(), supplying the full line of input entered by the user. - Within
parser.parse(),parser.extractArgs(input)is called, which processes the string into aHashMap<String, String>variable.
In this instance, the hashmap contains the following entries:
| Key (String) | Value (String) |
|---|---|
| null | edit 123 |
| t | Harry Potter |
- Since the command word
editis detected, a newEditCommandobject is returned by theparser. - The
execute(ui, catalogue)method ofEditCommandis called, which further calls thehandlesEditCommand(ui, catalogue)method. - In the
handlesEditCommand(ui, catalogue)method, theprocessArgs(catalogue)method is called, which processes the value associated with thenullkey, to check if the user inputted a valid item id and to retrieve the item associated with that id from the catalogue. - In this case, since a valid
Bookobject with id 123 exists in the catalogue, a newEditBookCommandobject is created, which then calls its ownexecute(ui, catalogue)andhandlesEditBookCommand(ui, catalogue)methods. - The method
processArgs()is performed to extract “Harry Potter”, the new title of the book. Checks are also performed to ascertain if the attribute to be edited is missing, if there are no valid arguments supplied, or if invalid arguments are supplied, outputting the relevant warning messages for each. - In this case, since all checks pass, the
setTitle(title)method of the existingBookobject with id 123 is called, and itstitleattribute is edited to “Harry Potter”.
Search Command
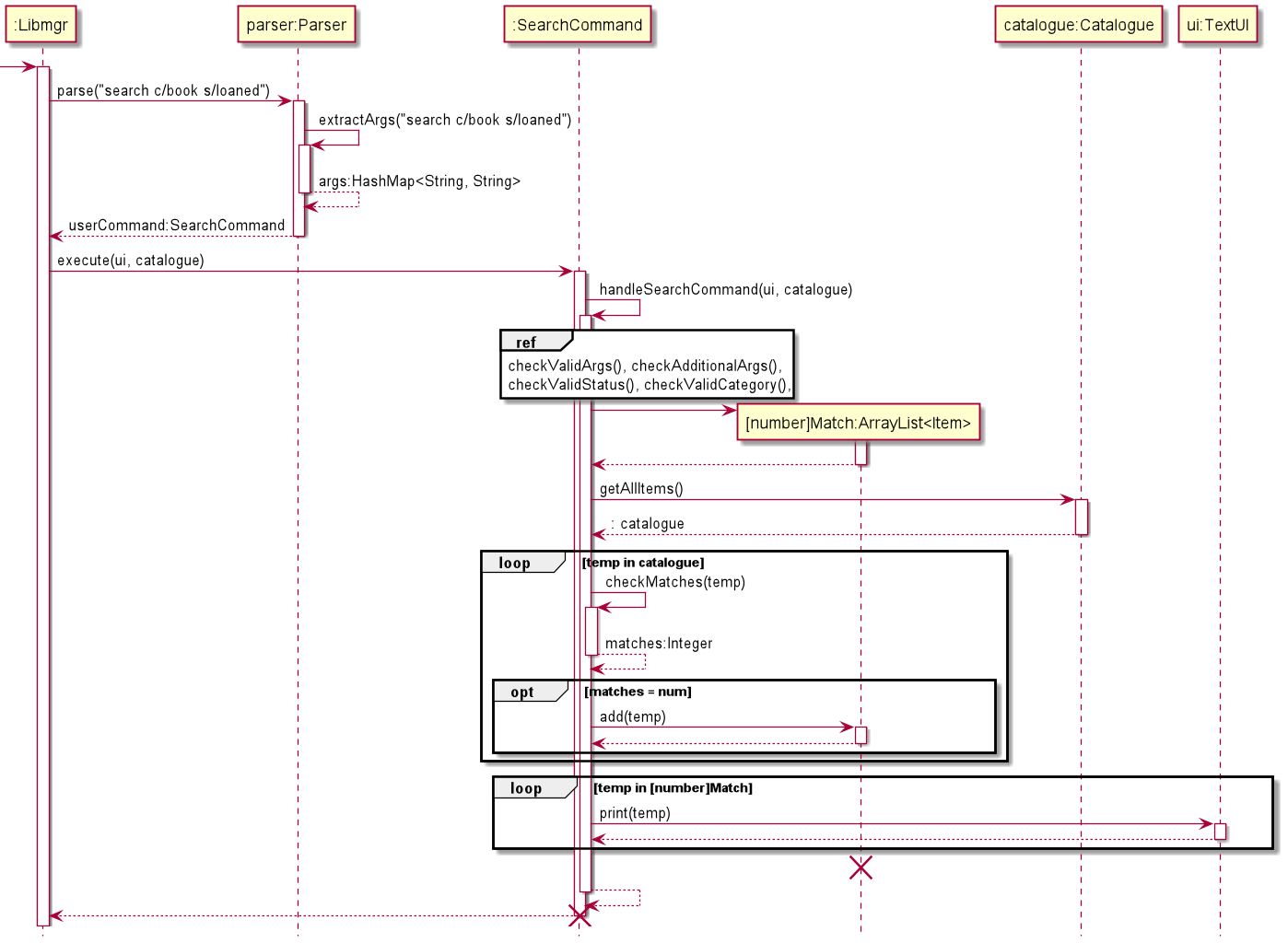
The Search class handles the functionality to search items based on multiple searching keywords. Such keywords include “id”, “category”, “status”, and “title”. This sequence diagram shows the interactions occurring when the command “search c/book s/loaned” is executed.
Libmgrcallsparse()method inparserobject, which returns a searchCommand object.Libmgrcallsexecute()method insearchCommandobject, which calls ahandleSearch()in itself.searchCommandperforms several checks on the args, by calling several methods.searchCommandcreates four ArrayList ofItemcalled [num]Match, i.e., fourMatch/threeMatch/twoMatch/oneMatch respectively.searchCommandcallsgetAllItems()method incatalogueobject, which returns an ArrayList of all objects incatalogue.searchCommandloops through all items fromcatalogue, callscheckMatches()method on each item.- Items with certain number of matches are inserted into one of the four corresponding [num]Match ArrayList.
searchCommandthen loops through each of four ArrayList, starting from fourMatch, ending with oneMatch, to print out all items in each ArrayList.
Loan Command
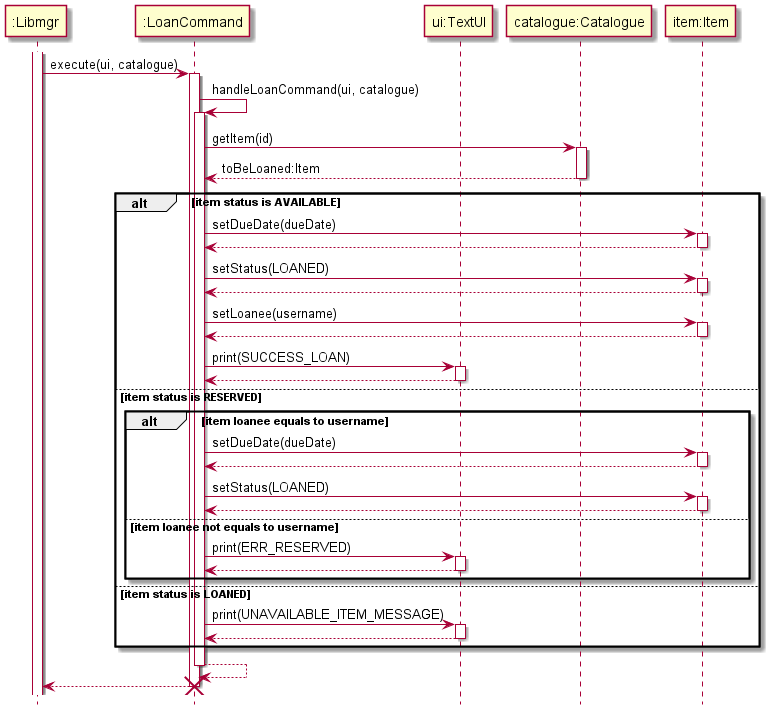
The Loan Command class handles the functionality to loan a specific item and change its attributes accordingly.
This sequence diagram shows the interactions occurring each time a user wants to loan an item.
Libmgrcallsexecute()method inLoanCommandobject.LoanCommandcalls thehandleLoanCommand()in itself.LoanCommandcalls thegetItem()inCatalogueusing the specific id given.LoanCommandchecks the status of the item.- When the item status is
AVAILABLEthe loan is successful and the item’s attributes change accordingly. - When the item status is
RESERVEDthe loan is successful only if the username matches the item’s loanee. - When the item status is
LOANEDthe loan is unsuccessful.
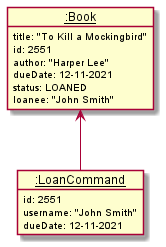
This object diagram shows an example when LoanCommand is being called to loan out a book with the details
shown in the diagram.
When the LoanCommand is executed, it will change the attributes of this book such that:
status: nullchanges tostatus: LOANEDloanee: nullchanges toloanee: "John Smith"dueDate: nullchanges todueDate: 12-11-2021
Deadline Command
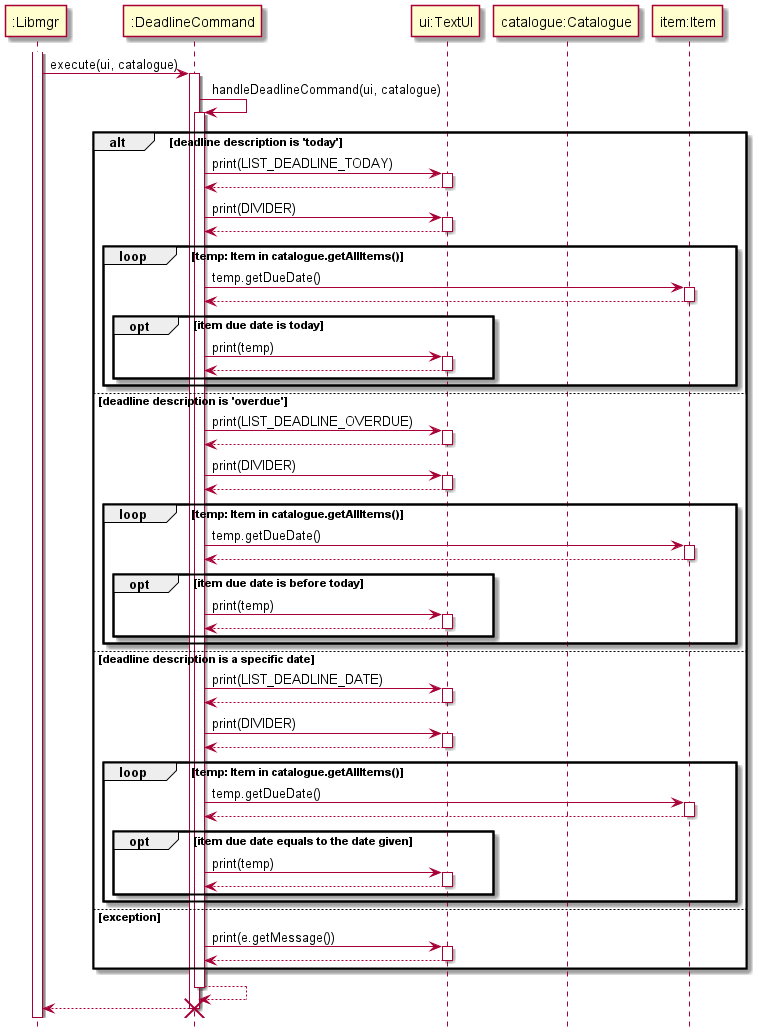
The Deadline Command class handles the functionality to list the items according to their due dates.
This sequence diagram shows the interactions occurring each time a user wants to loan an item.
Libmgrcallsexecute()method inDeadlineCommandobject.DeadlineCommandcalls thehandleDeadlineCommand()in itself.DeadlineCommandchecks the description of the command given by the user.- If the deadline description is
today, it will print all items that are due today. - If the deadline description is
overdue, it will print all items that are overdue (due before today). - If the deadline description is a specific date, it will print all items that are due by the date given.
- If the deadline description is outside the listed three above, it will throw an exception and print the error message accordingly.
Storage Processes
Reading from file and deserializing
When Libmgr is started at each runtime, it performs an operation to find existing data.json file within a specified directory, and attempt to load in the data stored within into the catalogue.
The following sequence diagram shows the process of reading from the data file, along with an explanation of the steps.
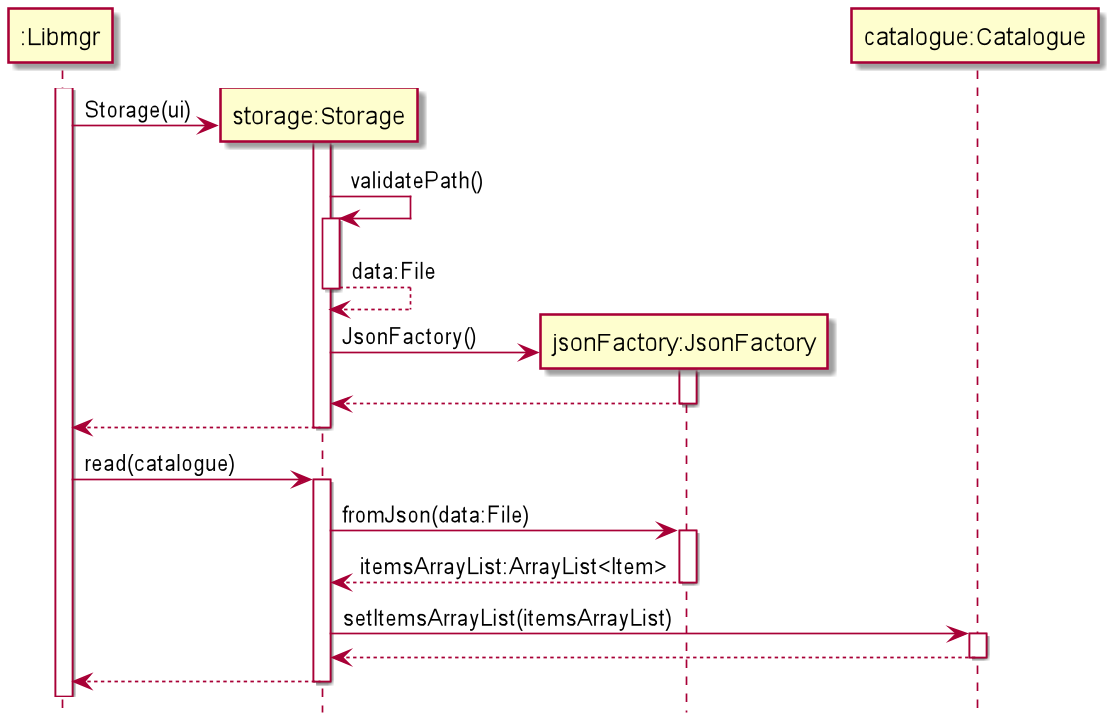
- Within
Libmgr.main(), when the program is first started, it creates a newStorageobject. - The
Storageobject then attempts to confirm the presence of the data file in the specified directory- If the file exists, it returns a java
Fileobject pointing todata.json - If the file does not exist, it creates a new
data.jsonfile in the default directory and stores an empty catalogue within
- If the file exists, it returns a java
- Afterwards, the
Storageobject creates a newJsonFactoryobject. - Lastly,
Libmgr.main()callsStorage.read()which reads data from thedata.jsonfile and callsjsonFactory.fromJson()to deserialize the data within into an array list of items. If thedata.jsonfile contains errors, is malformed or corrupted, the user will be informed. - This array list is then passed as an argument when the
catalogue.setItemsArrayList()method is called, recreating the previous state of the catalogue
Serializing and writing to file
Upon the completion of every command input by the user, libmgr will serialize the contents within the catalogue and store it in data.json.
This ensures that an up-to-date copy of the catalogue is always recorded into data.json.
The following sequence diagram shows the process of serialization and writing to file, along with the explanation of the steps.
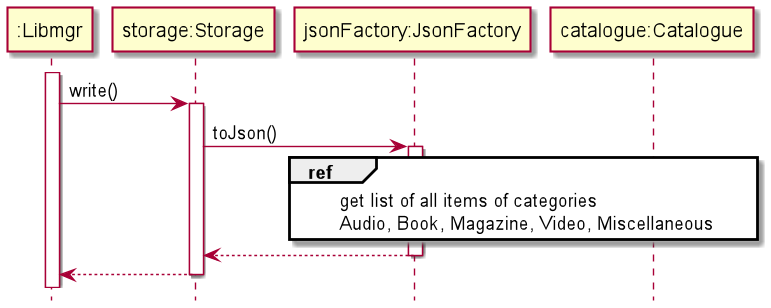
- After completing execution of each command,
Libmgr.main()will call thestorage.write()method in order to store the current state of the catalogue. - The
Storageobject in turn callsjsonFactory.toJson()for each of the five item types (audio, book, magazine, video, miscellaneous) in order to serialize all items within the catalogue - The
Storageobject then outputs the data inJSONformat todata.jsonthrough a javaFileWriterobject.
ℹ️ The default directory where
data.jsonis located is./data/data.json
This can be modified within theStorageclass.
ℹ️ Users and developers are allowed to manually edit the
data.jsonfile with tools such as text editors, but are strongly recommended to exercise caution regarding formatting and spelling, as a small error can result in corrupting the entire file’s structure.
⚠️As the
data.jsonfile is updated after completing execution of each command, if a corrupteddata.jsonfile is loaded and the user/developer wishes to retain the file, terminate the programme immediately, do not execute any commands other thanexit
⚠️ Do not make changes to the
data.jsonwhilelibmgris running. Any changes made while running will not be reflected bylibmgrand such changes may be overwritten.
Appendix A: Product scope
Target user profile
Library staff who prefer keyboard inputs and require a text based application to quickly track and update the details of library items within their catalogue.
Value proposition
This product aims to streamline the process of managing the book catalogues within their library. It will allow library staff to track their items, such as finding out their status, as well as update their catalogue quickly. Designed for fast typists, it also allows staff to track, update and manage their inventory more efficiently.
Appendix B: User Stories
| Version | As a … | I want to … | So that I can … | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| v1.0 | librarian | add items to the catalogue | keep the full catalogue up to date | |
| v1.0 | librarian | remove items from the catalogue | keep the full catalogue up to date | |
| v1.0 | librarian | update the status of an item when it is loaned out | keep the full catalogue up to date | |
| v1.0 | librarian | update the status of an item when it is returned | keep the full catalogue up to date | |
| v1.0 | librarian | check the list of items available in the library | get an overview what items are still present within the library | |
| v1.0 | librarian | check the list of items on loan | expect what items are going to be returned soon | |
| v1.0 | librarian | check the list of all items in the library | get an overview of the full inventory of the library | |
| v2.0 | librarian | categorise different items into media forms. (E.g. book, magazine, audio, video) | better manage my catalogue | |
| v2.0 | librarian | edit the details of existing items on the catalogue | keep the full catalogue up to date | |
| v2.0 | librarian | reserve and un-reserve an item by updating its status | set aside an item for a user beforehand | |
| v2.0 | librarian | search for specific items by their title or ID | retrieve the details of items I need | |
| v2.0 | librarian | check the list of items on reservation | make an item available for others to loan | |
| v2.0 | librarian | loan an item for a person specified by their username | track who is in possession of a item currently | |
| v2.0 | librarian | reserve an item for a person specified by their username | ||
| v2.0 | librarian | view the list of items are due to be returned today | keep track of what items are expected to be returned today | |
| v2.0 | librarian | view the list of overdue items | inform people to return them | |
| v2.1 | librarian | view the list of items that are due to be returned on a specific date | get a list of expected returns in the future | |
| v2.1 | librarian | search items by their categories (Book, Audio, Magazine, Video) | easily sort through the inventory | |
| v2.1 | librarian | retain the items information | keep the details without re-entering it everytime I start the application | |
| v2.1 | librarian | search items using multiple parameters (title, id, status, category, etc) | narrow down the items based on certain parameters | |
| v2.1 | librarian | edit the details of the items simultaneously | quickly make changes to the details of each item | |
| v2.1 | librarian | track miscellaneous items | also record items that are not categorised as audio, books, magazines or videos | |
| v2.1 | librarian | display the information of the library stats | get a rough gauge about the usage of the library’s assets | |
| v2.1 | librarian | access a help guide on how to use the app quickly | use the app more effectively in my job |
Appendix C: Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on Windows, macOSX and Linux as long as it has Java 11 or above installed.
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
Appendix D: Instructions for manual testing
Launch and Shutdown
- Initial Launch
- Download the latest
libmgr.jarand move it into a separate directory or folder - Ensure that Java 11 has been installed and configured on your device.
- Open a command prompt or terminal and run the command
java -jar libmgr.jar.
- Download the latest
- Shutdown
- Type
exitto quit the program.
- Type
Loading Data
If you wish to start the program while retaining data:
- Within the folder that contains
libmgr.jar, create a subdirectory calleddata. - Ensure that the JSON file containing the program data is named
data.jsonand move it to thedatasubdirectory. The full path should be./data/data.json - Start the program with the command mentioned above.
⚠️ If the program shows an error regarding malformed or corrupted data files, and you wish to retain the current state of the data file, exit the program immediately and do not run any other commands, otherwise, the data file may be overwritten. Afterwards, use a text editor to make any changes before restarting the program.
Running Commands
Refer to the list of commands shown in the user guide. Alternatively, type help to get an overview of the list of commands and their usage.